Levels of Incontinence
Associated with
STRESS OF INCONTINENCE
Recommended Products
-

Pantiliners
-

Bladder Control Pads
-
Male Guards
-
Pant Liners
Stresss Incontinence can effect both men and women. Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI) occurs because of weak pelvic floor muscles and/or a deficient urethral sphincter. This weakness can cause the bladder to leak during exercise, coughing, sneezing, laughing, or any body movement that puts pressure on the bladder. SUI often shows up after childbirth and menopause in women while prostate cancer treatment, such as radical prostatectomy, can trigger it in men.
Common Causes
• Strenuous physical activities
• Pregnancy and childbirth
• Pelvic surgery and trauma
• Loss of muscle tone
• Enlarged prostate
• Shift in hormonal balance with women
Moderate Bladder Leakage
Associated with
URGE & MIXED INCONTINENCE
Recommended Products
-
Underwear For Women
-
Underwear For Men
-
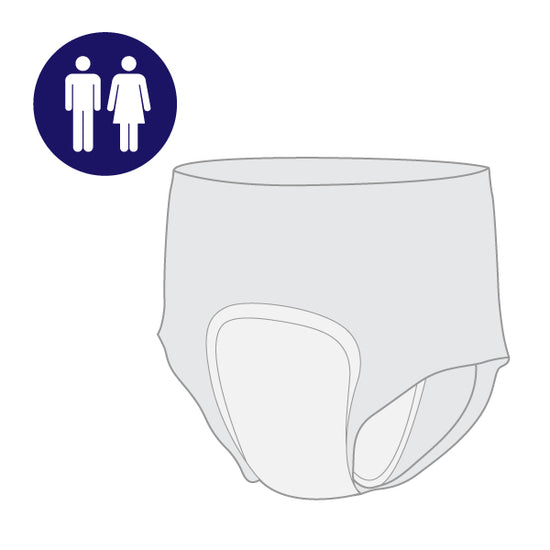
Protective Underwear
Urge Incontinence is associated with an Overactive Bladder (OAB). Spontaneous bladder spasms and contractions result in the frequent and sudden need to urinate. Frequent, strong and sudden urges happen with not enough time to make it to the bathroom.
Common Causes
• Bladder stimulants & irritants such as alcohol, caffeine and carbonated drinks
• Medications such as sedatives, cold medicines and high blood pressure medicines
• Urinary Tract Infections (UTI) and cancer
• Nerve Dysfunction associated with Trauma, Diabetes, Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury,
Alzheimer’s, Parkinsonism, etc.
• Shift in hormonal balance with women
Mixed Incontinence is a combination of the symptoms of stress incontinence and overactive bladder. It is important to note that intentionally urinating frequently to try to prevent stress-related leakage can result in shrinking of the bladder, limiting its ability to hold enough urine.
Common Causes
• Mixed incontinence occurs when symptoms of both stress and urge types of incontinence are present
Heavy Bladder Leakage
Associated with
OVERFLOW & FUNCTIONAL INCONTINENCE
Recommended Products
-
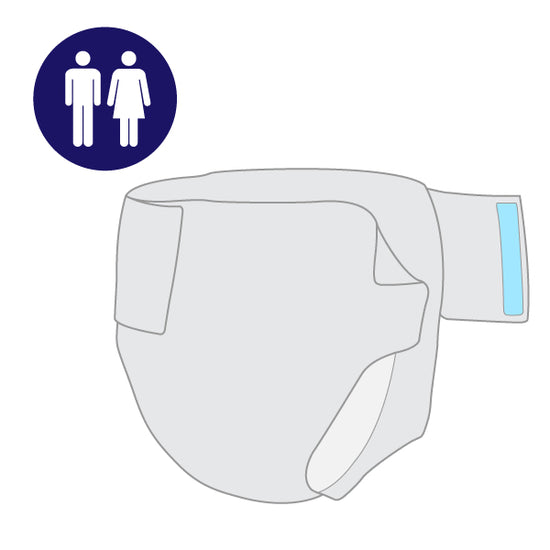
NGB Briefs
-
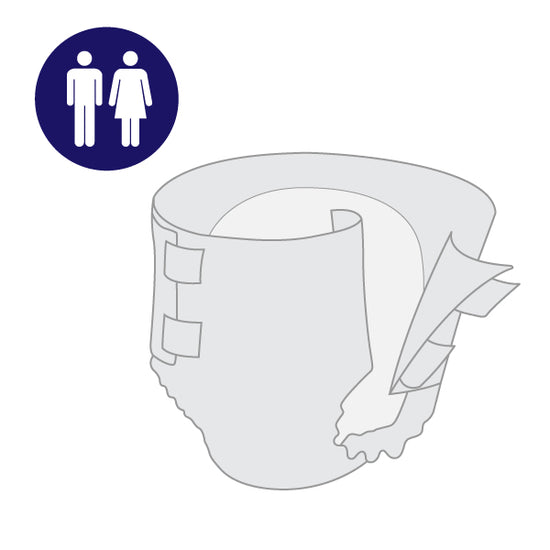
Adult Briefs
-
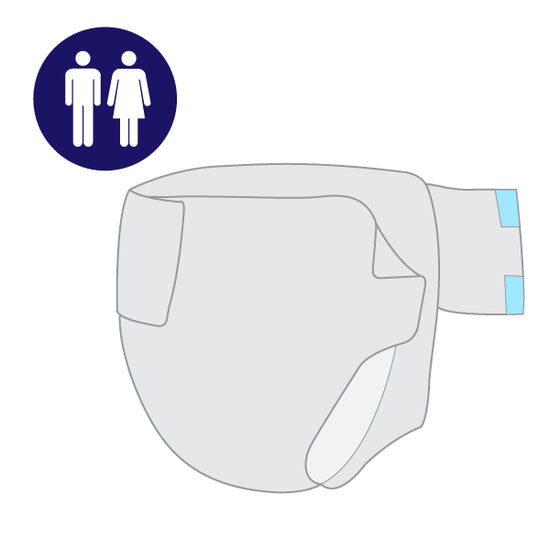
Extended Use Briefs
-
Bariatric Briefs
Overflow Incontinence results in the feeling of a full bladder. One fails to sense a full bladder because of nerve damage and thus does not empty the bladder. Constant dribbling of urine is a frequent symptom. There is increased frequency and urgency to urinate.
Common Causes
Blockage of the natural passageway of urine resulting from:
• Bladder injury
• Radical pelvic surgery
• Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
• Nerve damage from diabetes
• A narrowing of the urethra
• Medications
Functional Incontinence occurs when the urinary system may work well, but factors outside the urinary tract, such as immobility or cognitive impairment, can prevent a person from getting to a bathroom in time.
Common Causes
• Functional disability and psychological impairment
• Physical and mental disabilities, such as immobility or cognitive impairments
• Environmental barriers, such as stairs, clothing, or wheelchair accessibility














